Владыки (Vladyki)
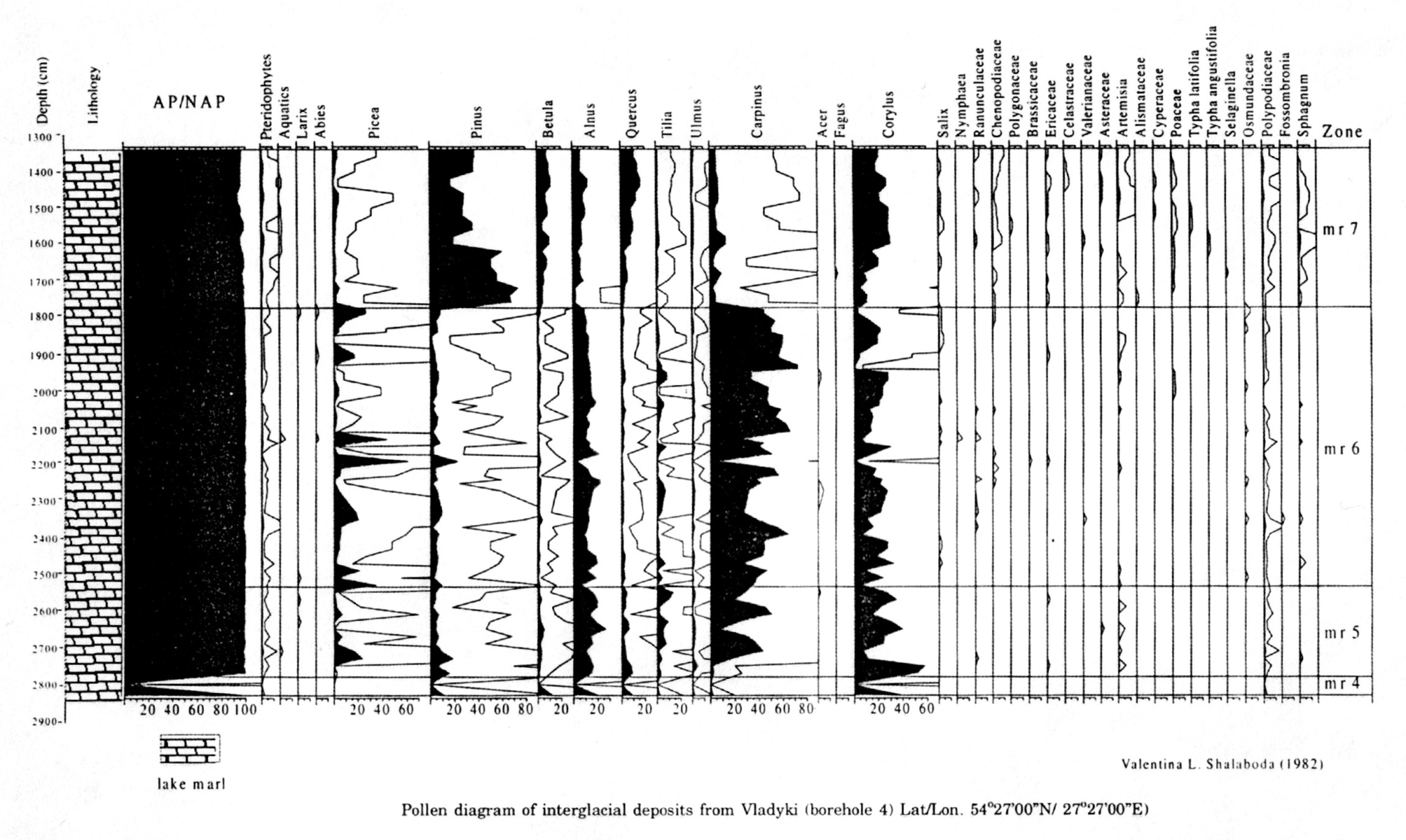
Spore-pollen analysis revealed the regional features of the vegetation communities forming. The percentages of all the AP and NAP taxa have been calculated of the total pollen sum AP+NAP (AP = pollen sum of trees and shrubs; NAP = pollen sum of upland herbs). The percentages of the pteridophytes and aquatics have been calculated of the total pollen sum. Indication of the pollen zones has been fulfilled according to the scheme of Makhnach et al. (1981) with some corrections based on more recent investigations.
DESCRIPTION OF THE POLLEN ZONES
MURAVIAN (=EEMIAN, MIKULINSKI) INTERGLACIAL
mr4 — Quercus-Pinus-Corylus
Maximum of Quercus along with an increasing percentages of Corylus and decreasing participation of Pinus is a common feature of this zone over the whole study area.
mr5 — Corylus-Tilia-Alnus
Arboreal species dominate while the herb plants are few. Synchronous maxima of Tilia and Alnus, preceded by the maximum of Corylus are characteristic of this zone. In most sections these events take place against a background of an increasing role of Carpinus. In Vladyki, increase of Polypodiaceae values and sporadic grains of Pinus, Betula, Ulmus were recognized. In Vladyki high values of Picea are present.
mr6 — Carpinus
The principal feature of this zone is the maximum of Carpinus, the presence of Picea and, increase of its percentage by the end of the zone. In Vladyki, the values of Alnus, Corylus, Pinus, Betula, Quercus and Tilia, remain more or less stable while amounts of Picea fluctuate. Arboreal species dominate but Polypodiaceae are also present.
mr7 — Pinus-Carpinus-Corylus I Pinus-Corylus-Quercus-Carpinus
This zone is characterized by the maximum of Pinus and by the second (small) peak of Carpinus.
Shalaboda V.L. Characteristic features of Muravian (Eemian) pollen succession from various regions of Belarus // Acta Paleobotanica. 41(1). 2001. Pp. 27-41.